Doctorate course
Analysis of biological databases
Structural Biocomputing and Modeling Center
Research lines and Areas of Interest
The structural bioinformatics are applied to the study of human diseases in which the target can be treated either as a single molecule or as a protein complex, and where the available experimental data can be used to validate the predicted interactions. Spacial cases of study are the following:
1) The protein-protein interactions mediated by SH3 domains are involved
in transitory associations that produce multiaggregate complexes, which
in turn result in new interactions, the amplification and propagation of
the chemical signaling, the regulation of catalityc activity, or
facilitate the interaction between membrane and cytoskeleton. For these
reasons, the SH3 domains represent plausible and attractive therapeutic
targets for pharmacological intervention in a wide range of pathologies,
since they appear in ceretain key signal proteins, such as Lyn y Hck in
AIDS; Lyn, in allergy and asthma; Gbr2 and Src in breast cancer; p85,
Grb2 y Gap in cancer, Abl, Grb2 y CrkL in chronic myelogenous leukemia;
p47-phox y p67-phox in inflammatory diseases; Src in osteoporosis; Tec
in the myelodysplastic syndrome; Btk in pre B cellular leukemia, etc.,
as well as the localization and regulation of ionic channels (Na channel
in Liddle syndrome, Ca channel regulated by domains SH3-GK or the
association of the K channel Kv1.5 with Src tyrosine kinase, etc.
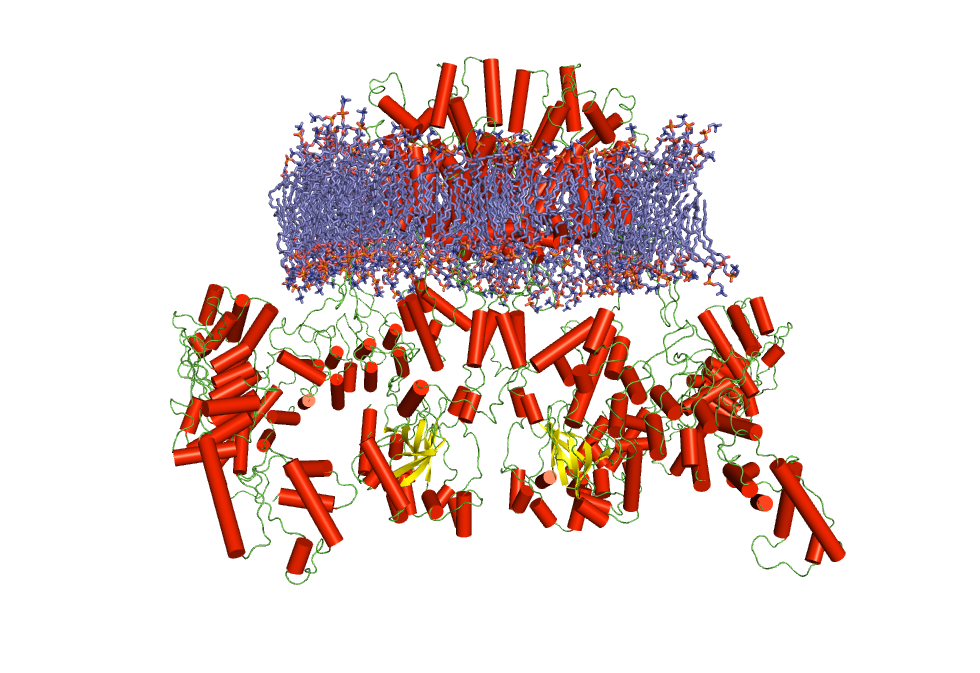
2) Molecular modeling of soluble and membrane protein, in complex with
ligand, effectors or expands the available tridimensional data by
homology modeling. This technique is used to model complex receptors and
channels, as is the case of the TRPV1 or the nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor channels, and the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, belonging
to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family. The use of homology modeling
in combination with Molecular Dynamic approaches allows the simulation
of membrane proteins in its native membrane environment, including
lipids, water molecules and ions.
3) The combination of Structural Proteomics and Bioinformatics can
undergo the creation of structural databases, as ADAN
(http://adan-embl.ibmc.umh.es) database, which contains a useful
collection of different modular protein domains (SH2, SH3, PDZ, etc.)
mainly involved in protein-protein interactions. The database contains
more than 2500 entries comprising protein interactions domains, enzymes
and derived models that are manually integrated and annotated to provide
biological and functional information. The database offers as a novelty
the position specific scoring matrices, used to predict optimum ligands
and to search putative partners in the entire genome.
Finally, computational protein engeneering can provide putative
interactors able to modify/regulate the multiprotein complex behaviour
by competition, thus being a useful tool in pharmacological intervention.
Research Keywords
Computational Protein Design
Protein-Protein Interactions
Structural Proteomics
Molecular Modeling of Soluble and Membrane Proteins
Financed Projects
Identificación de ligandos y especificidad de dominios SH3
implicados en patologías humanas.
Bancaja. Ref.: UMH 0042/06. 2006-2007.
Localización de ligandos específicos de dominios SH3
implicados en la formación de complejos multiproteína.
Generalitat Valenciana. Ref.: GV/2007/025. 2007-2009.
Contrato de asesoramiento y asistencia en el desarrollo de
la base de datos pública ADAN
Fundación Privada Centro de Regulación Genómica. Ref.: FUNDCRG1.07 A
Contrato de asesoramiento y asistencia en el desarrollo de
la base de datos pública ADAN
Fundación Privada Centro de Regulación Genómica. Ref.: FUNDCRG1.08 A
Contrato de asesoramiento y asistencia en el desarrollo de
la base de datos pública ADAN
Fundación Privada Centro de Regulación Genómica. Ref.: FUNDCRG1.09 A